Kubernetes Monitoring
Bindplane supports managing Kubernetes agents allowing you to streamline the observability of your cluster. Before following this guide, be sure to familiarize yourself with the Kubernetes Install, Upgrade, and Uninstall Agents documentation.
Objective
Monitoring a Kubernetes cluster involves collecting metrics and logs from various components that makeup the cluster.
Metrics
Kubelet
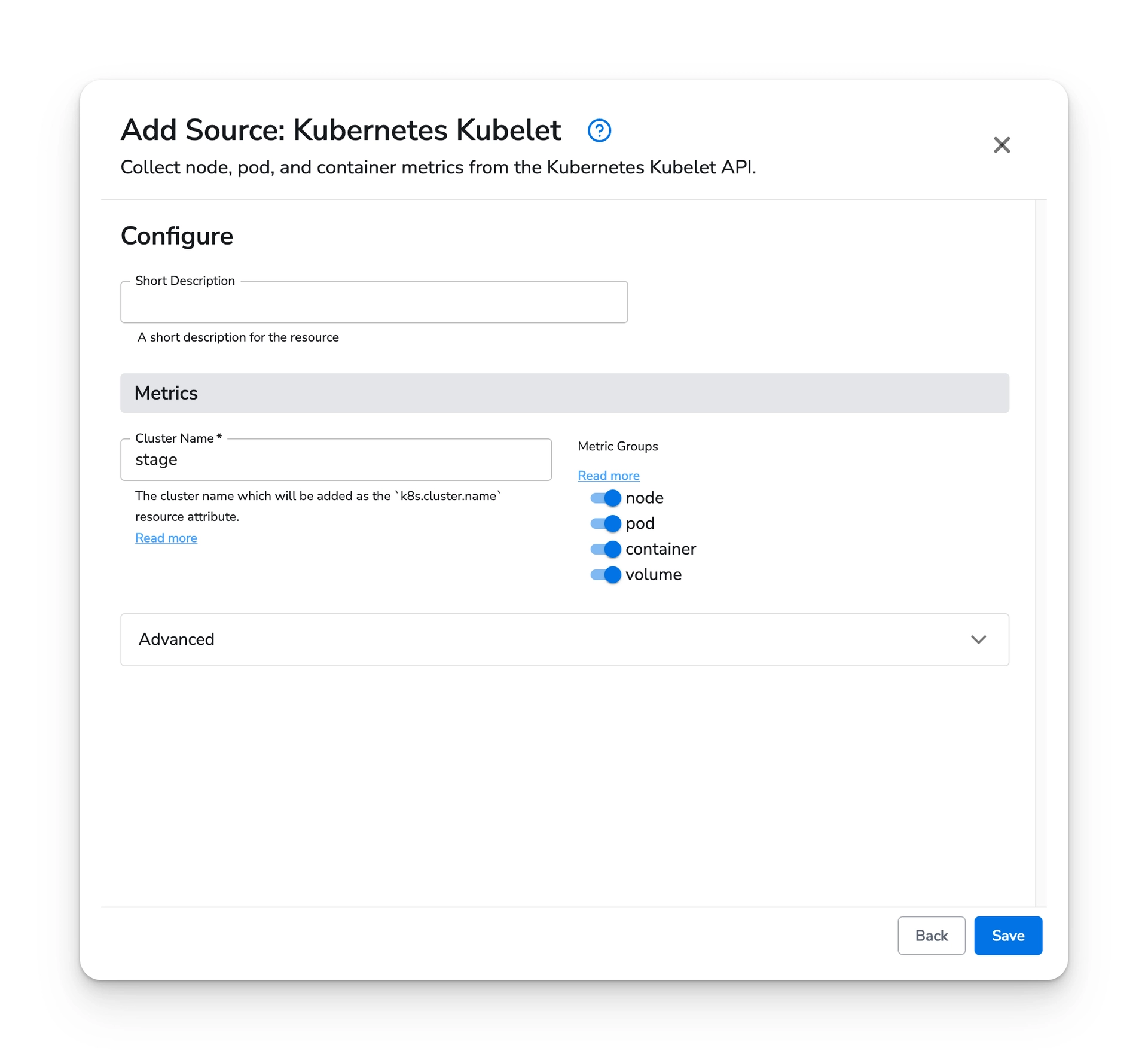
The Kubelet API is hosted on each node within the cluster. It can be used to gather node, pod, container, and volume metrics. Each Kubelet's scope is limited to the node it is running on.
The Kubelet API is useful for tracking pod and container performance metrics, such as CPU or memory utilization.
API Server
The Kubernetes API Server is hosted within the cluster as a Deployment. It can be used to gather higher-level cluster metrics, such as Deployment or Pod phase.
Logs
Container Logs
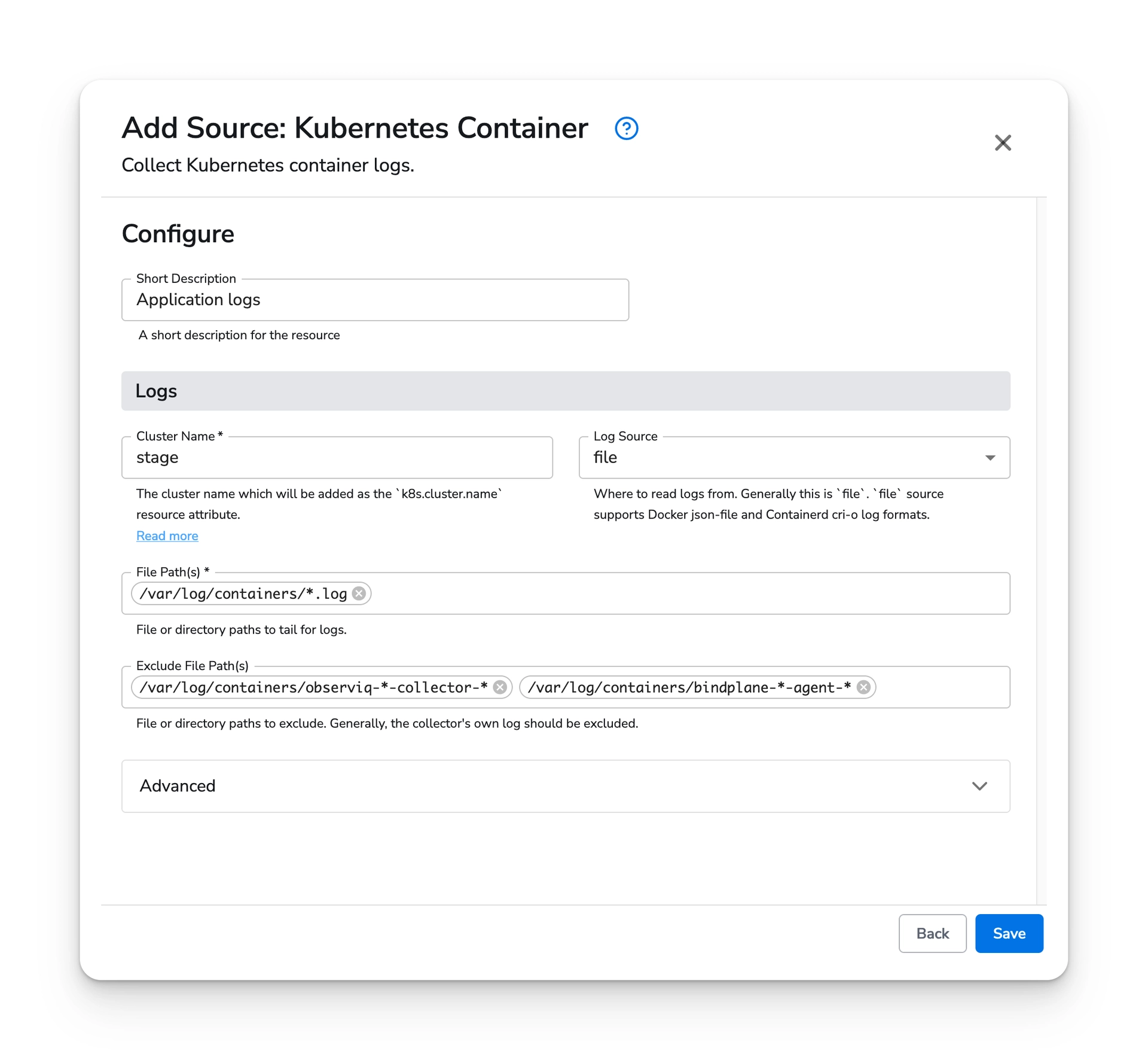
Kubernetes container logs are written to the node's filesystem. Each Kubernetes node is responsible for hosting these logs. Generally, the logs are written to /var/log/pods and are symlinked in /var/log/containers.
Each log file has the following format:
<pod name>_<namespace name> _<container name>-<container id>.logThe Bindplane Collector will extract metadata from the log file name following OpenTelemetry's Semantic Conventions.
Cluster Events
The Kubernetes API server can be used to retrieve Kubernetes Events in the form of logs.
Kubernetes Events are useful for observing issues such as pod crash loop event.
Tracing
Kubernetes does not emit traces, however, applications instrumented to emit OpenTelemetry traces are supported. See the OpenTelemetry section for details.
OpenTelemetry
If your applications are instrumented with OpenTelemetry, they can be configured to forward metrics, traces, and logs to the Bindplane Collectors.
Implementation
This guide will describe how to configure three configurations:
Kubernetes Node
Kubernetes Cluster
Kubernetes Gateway
The Bindplane Node and Cluster agents will forward their telemetry to the Bindplane Gateway agent(s) using a clusterIP service.
Prerequisites
You should have the following in place before moving forward with Bindplane Kubernetes Agent deployment.
Access to your Kubernetes cluster
Access to your Bindplane server
If you do not have Bindplane installed, you can follow one of these two guides for deploying Bindplane to a Linux server or Kubernetes.
Install Bindplane Server
Install Bindplane Server on Kubernetes
Create Configurations
Before agents can be deployed to the cluster, configurations must be created.
Node Configuration
On the Configurations page, choose "Create Configuration". Create a Kubernetes Node configuration. The node configuration will be deployed as a DaemonSet. The DaemonSet will allow the collection of container logs and Kubelet metrics from each node.
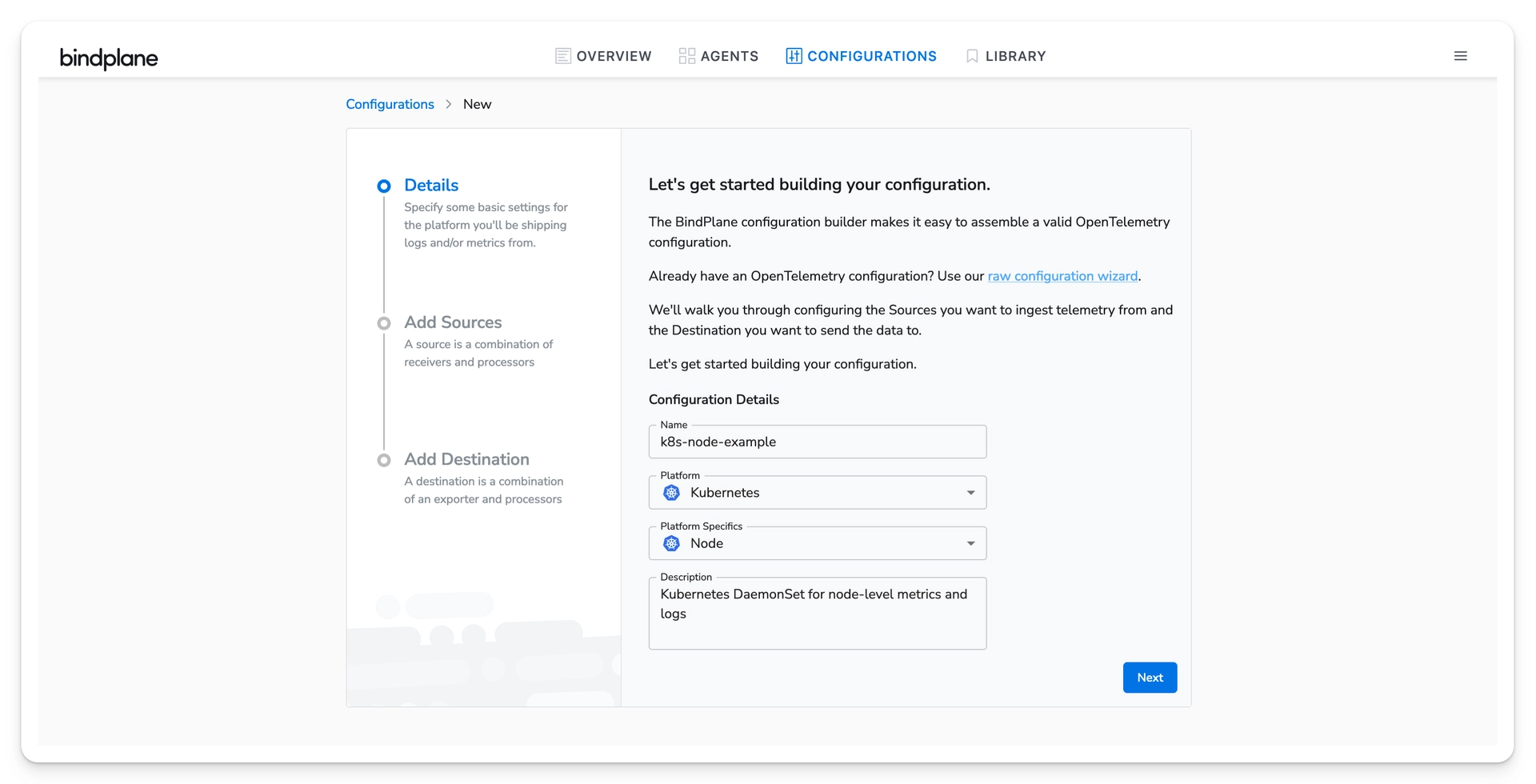
Choose next to view the list of available sources.
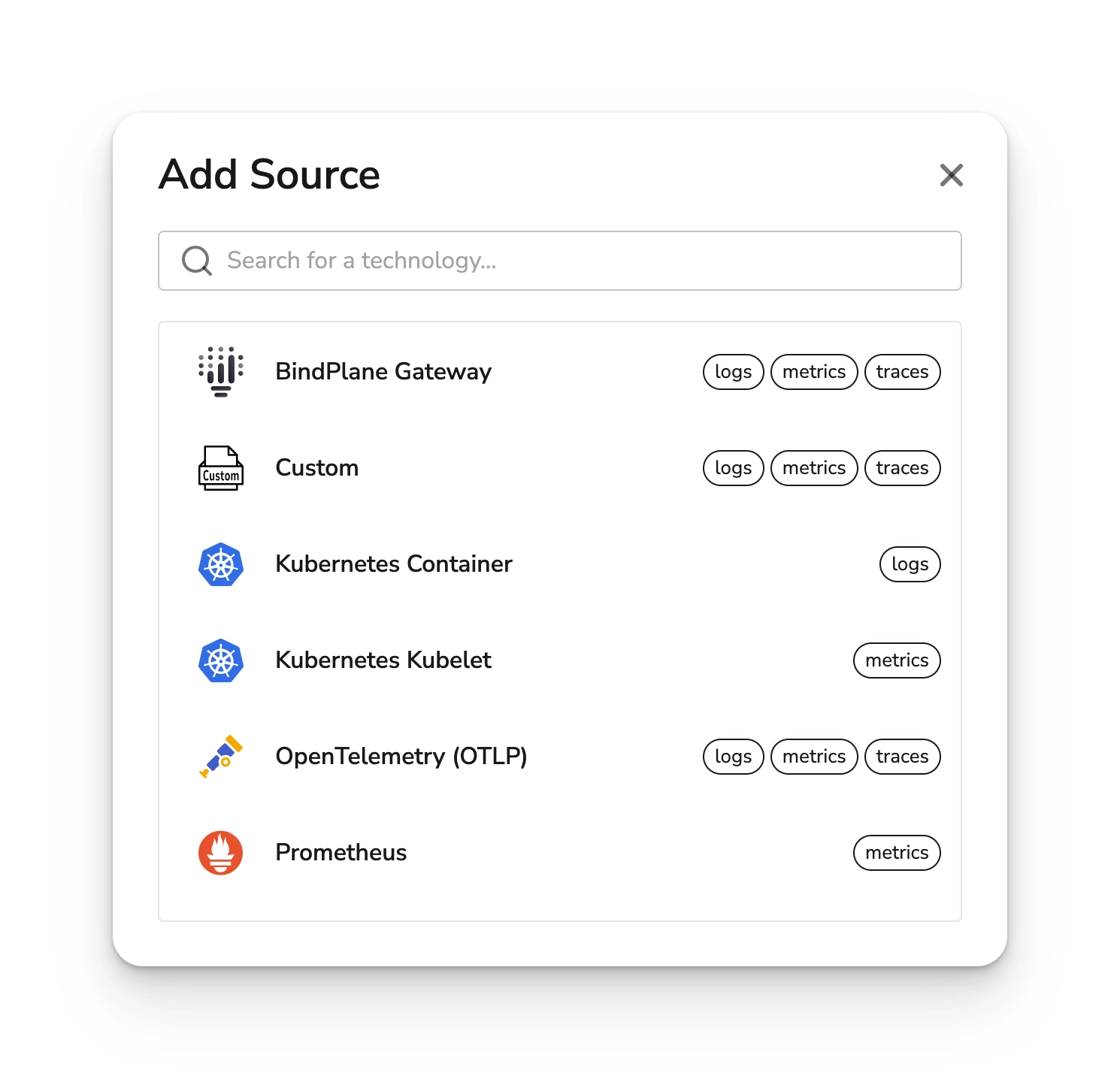
Select the Container source and configure it with a cluster name. You can use placeholder value if you intend to detect the cluster name using the resource detection processor. This processor can be configured during the gateway configuration setup.
Select the Kubelet source and configure it with a cluster name. You can use placeholder value if you intend to detect the cluster name using the resource detection processor. This processor can be configured during the gateway configuration setup.
Optionally, select the OpenTelemetry source. The DaemonSet can receive metrics, logs, and traces from applications in your cluster. If you would prefer to have your Gateway Agent handle receiving OpenTelemetry, you can skip this step.
At this point, you should have both Kubernetes sources and the OpenTelemetry (optional) source. Choose next to move to the destination configuration page.
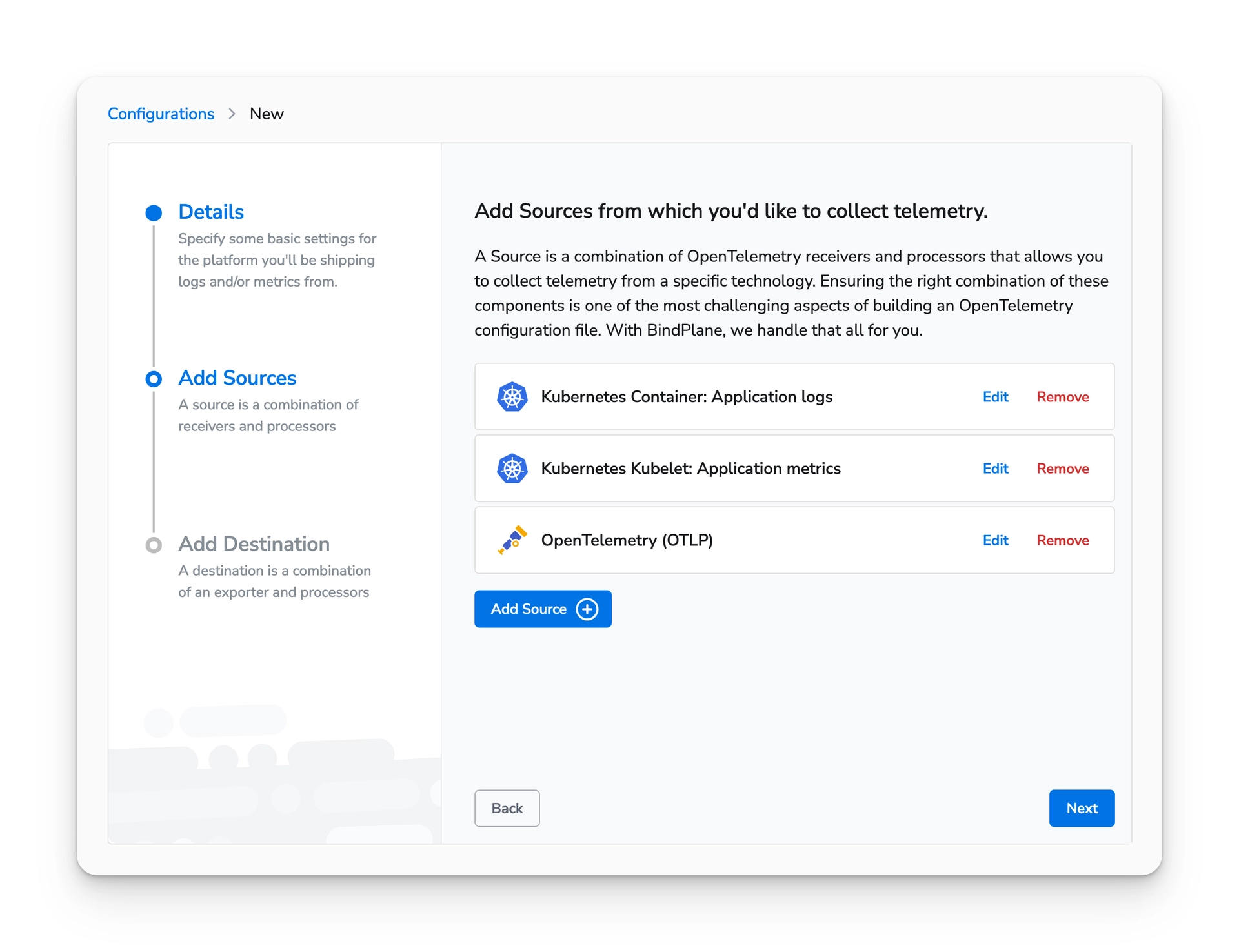
Search for "OpenTelemetry" and select the "OpenTelemetry (OTLP)" destination.
Configure the hostname field with the following value:
Leave all other options set to their default values.
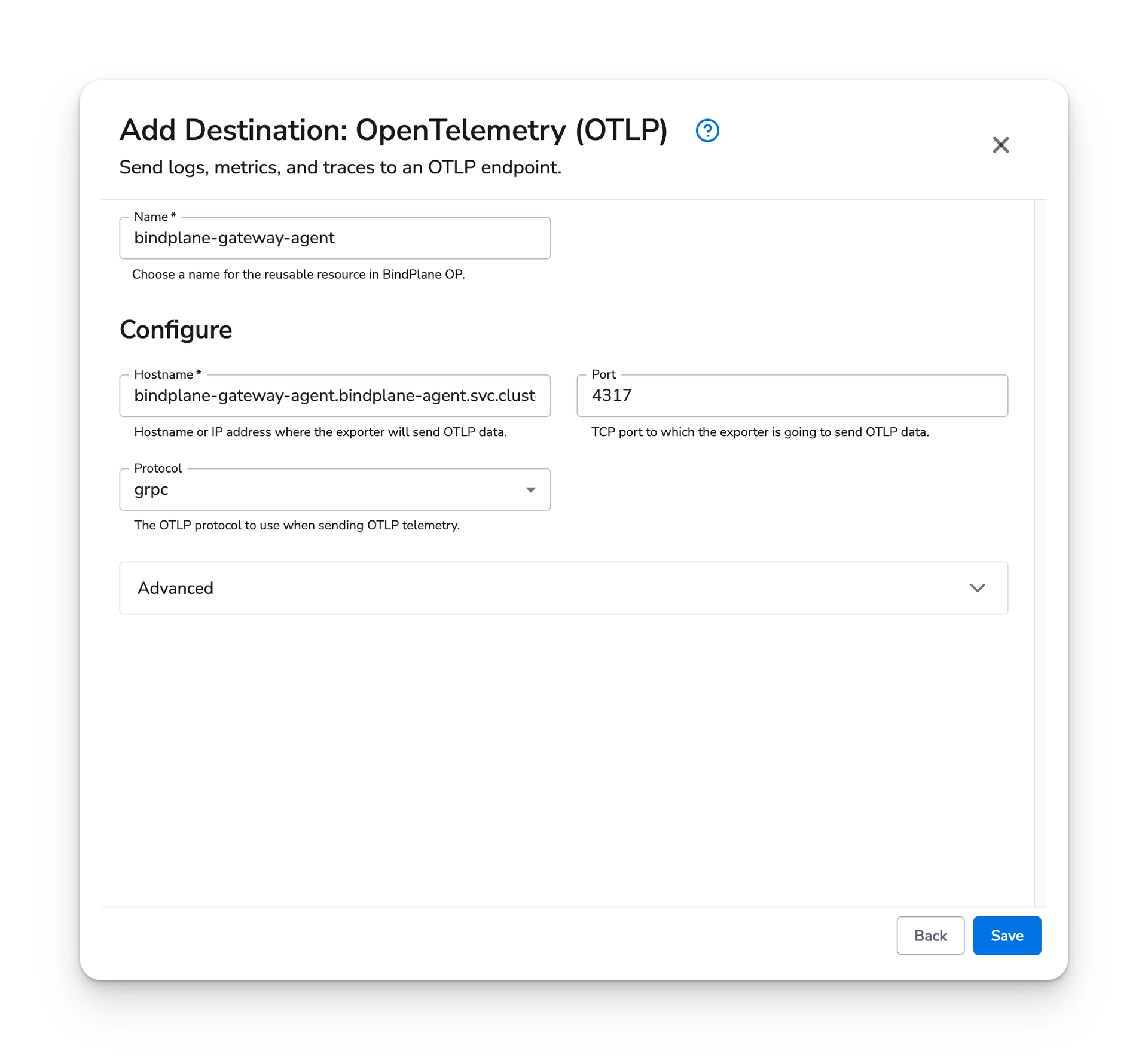
Once you have configured the destination, choose "Save".
You will be presented with the new pipeline.
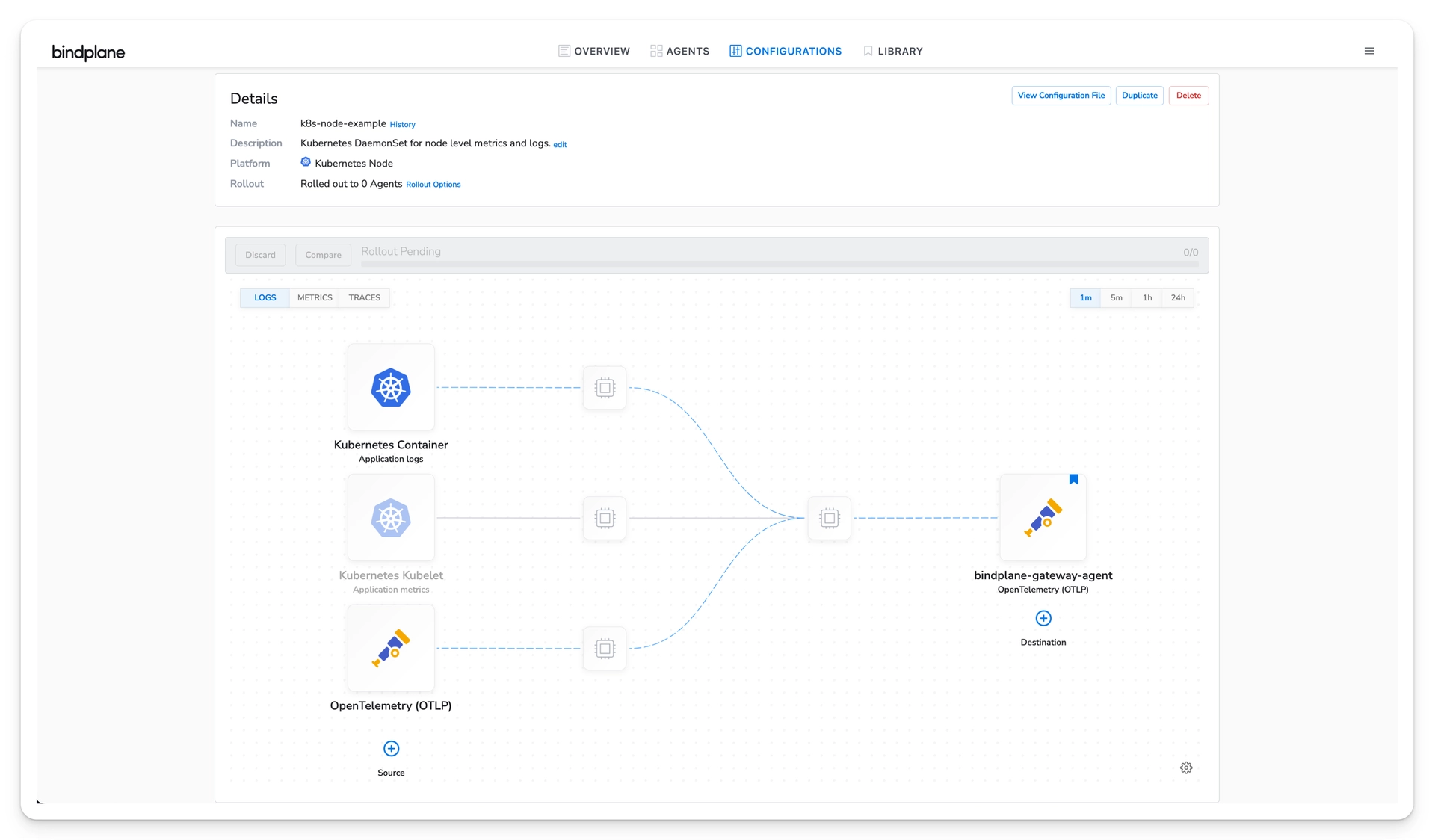
Cluster Configuration
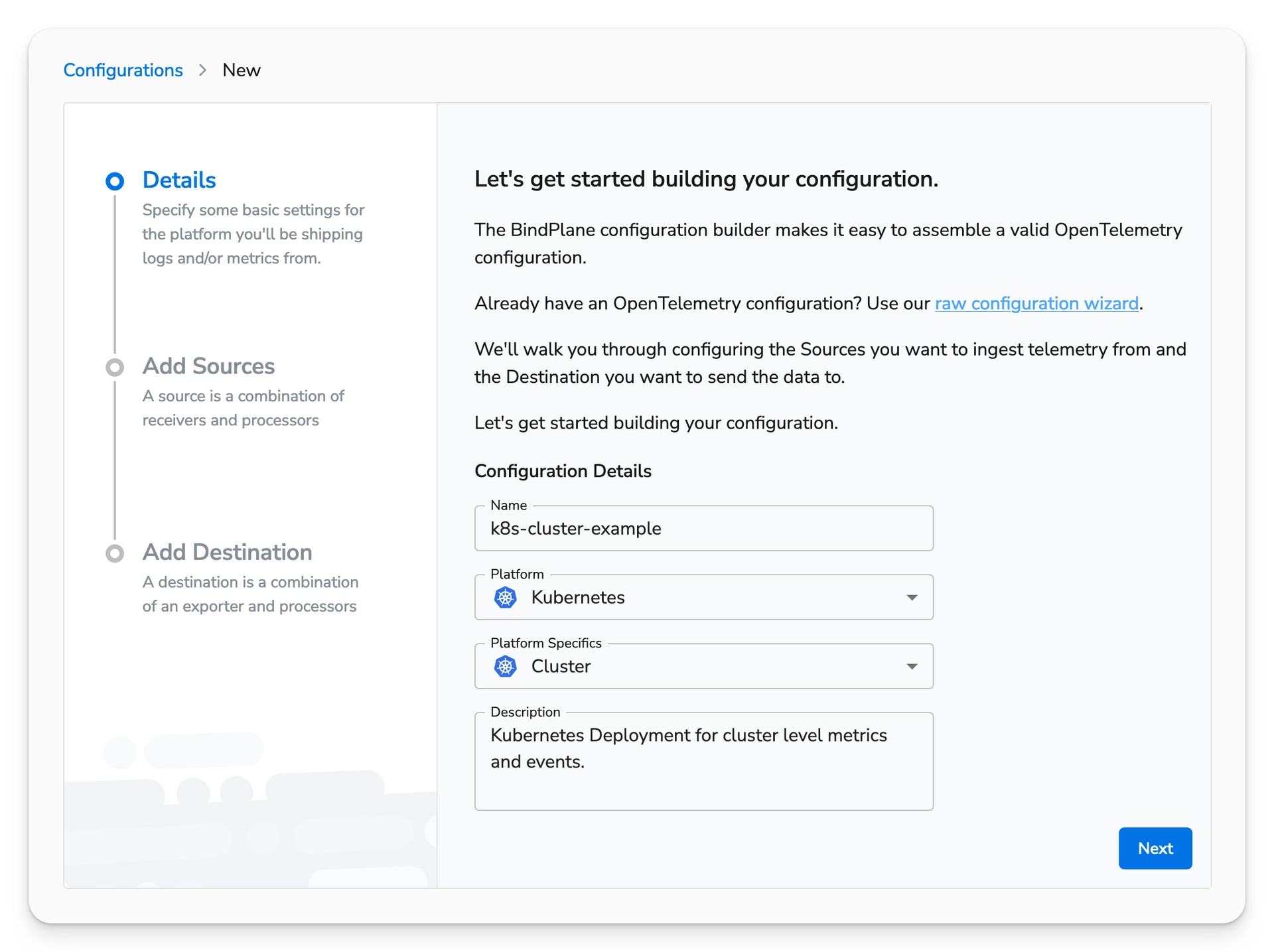
On the Configurations page, choose "Create Configuration". Create a Kubernetes Cluster configuration. The cluster configuration will be deployed as a Deployment with a single pod. The Deployment will allow the collection of cluster metrics and events (logs) from the Kubernetes API server.
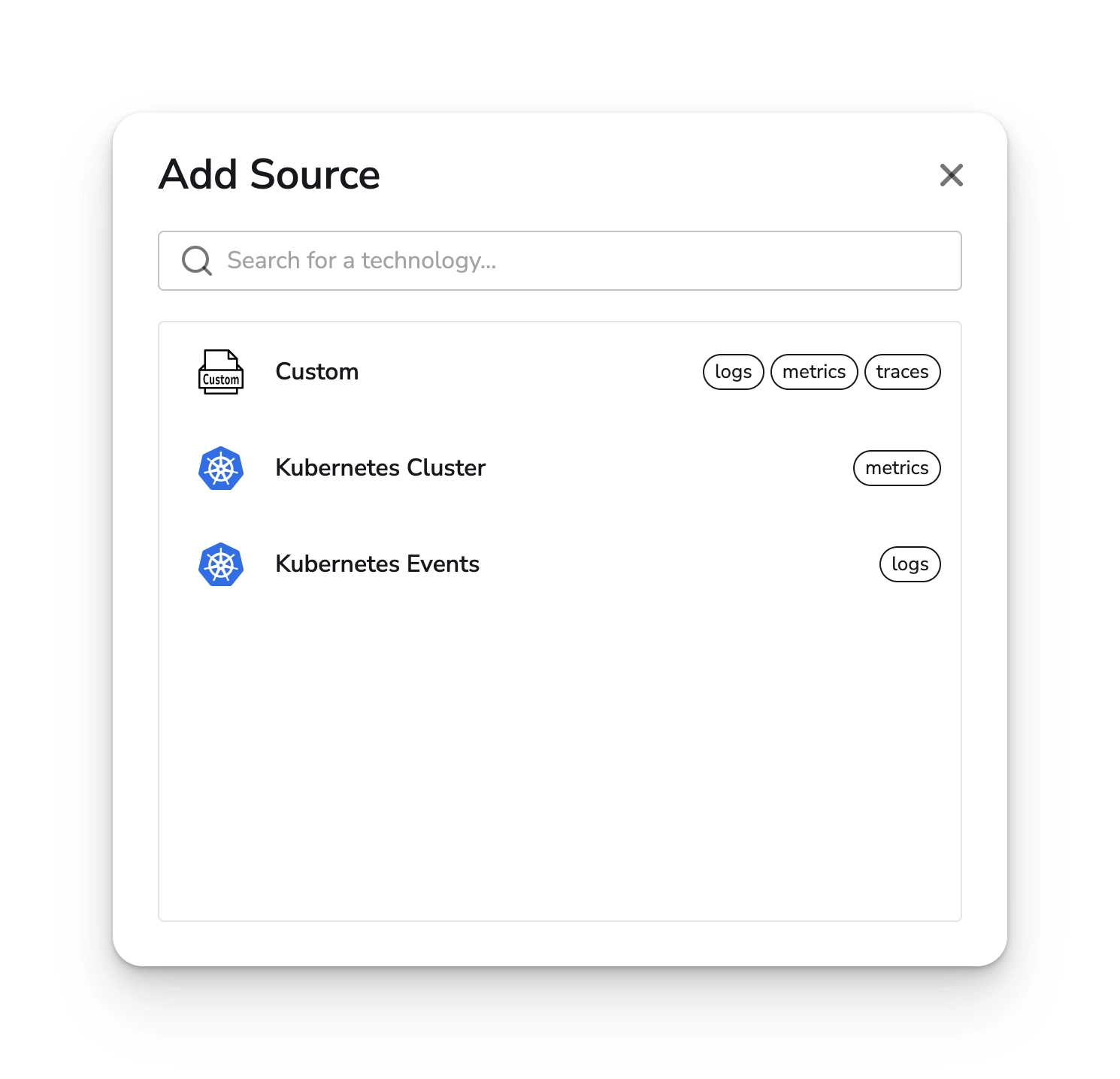
Choose next to view the list of available sources.
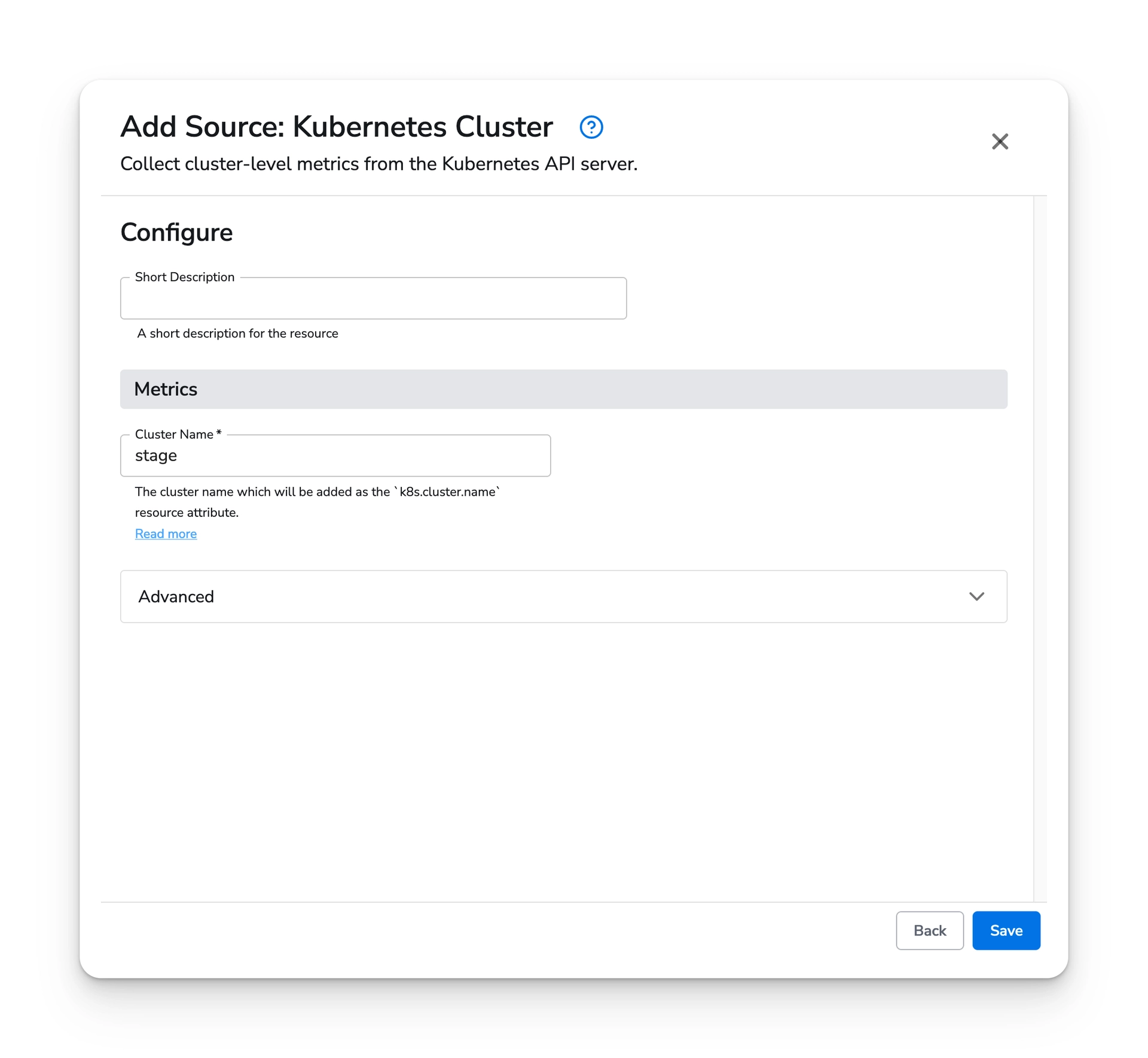
Select the Kubernetes Cluster source and configure it with a cluster name. You can use placeholder value if you intend to detect the cluster name using the resource detection processor. This processor can be configured during the gateway configuration setup.
Select the Kubernetes Events source and configure it with a cluster name. You can use placeholder value if you intend to detect the cluster name using the resource detection processor. This processor can be configured during the gateway configuration setup.
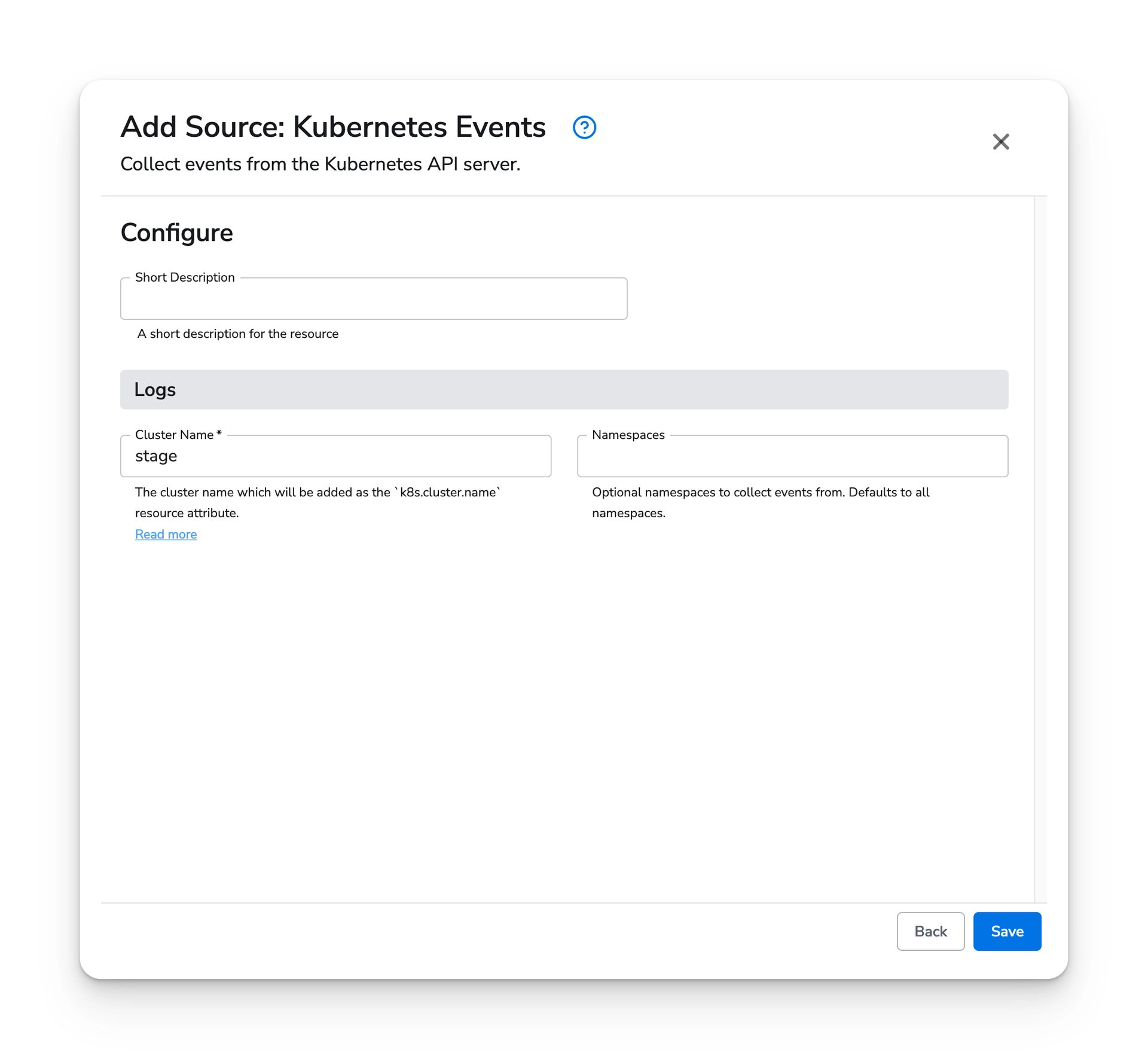
At this point, you should have both Kubernetes sources. Choose "next" to move to the destination configuration page.
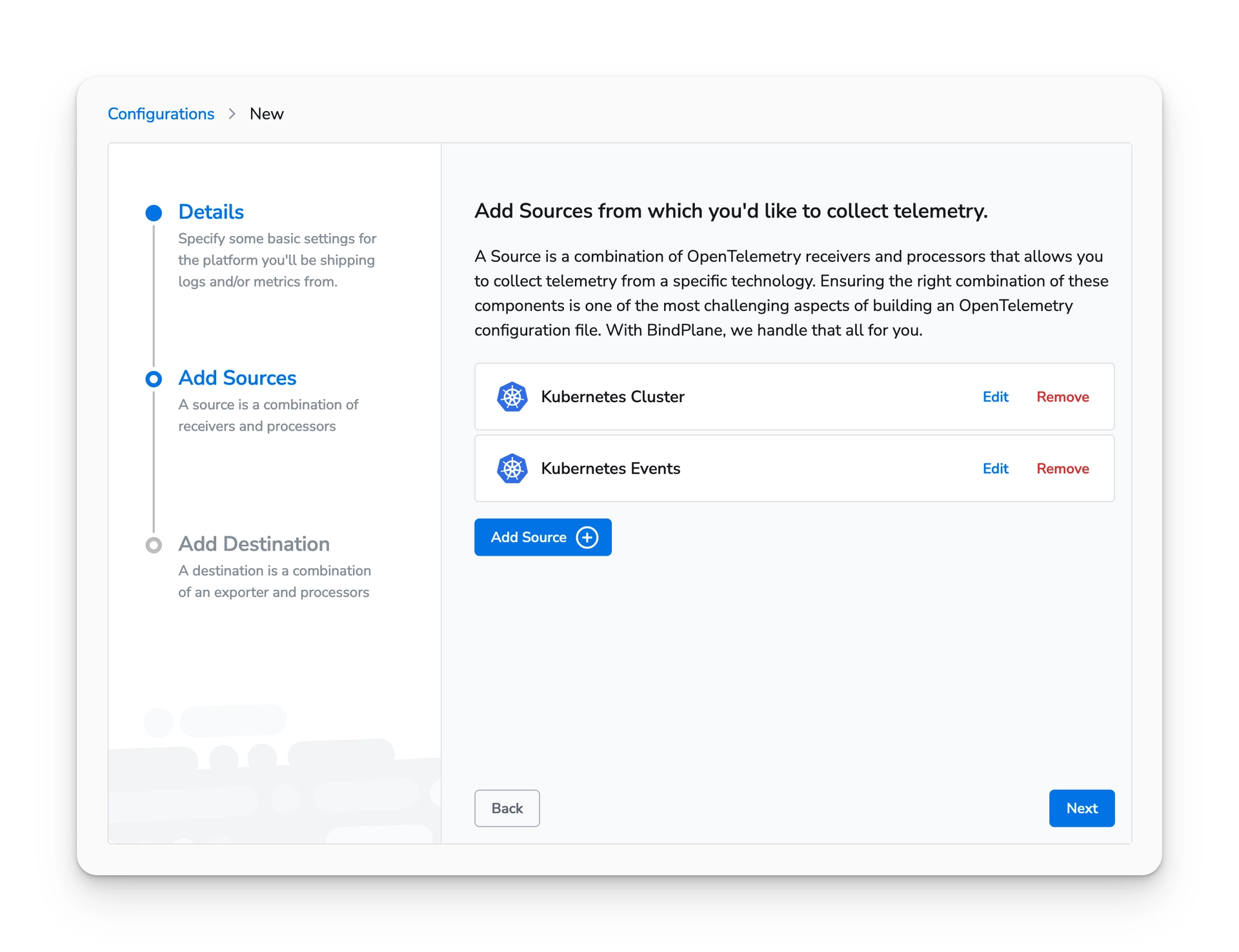
Select the same destination that you created for the node configuration and choose "Save".
Once the configuration is saved, you will be presented with the new pipeline.
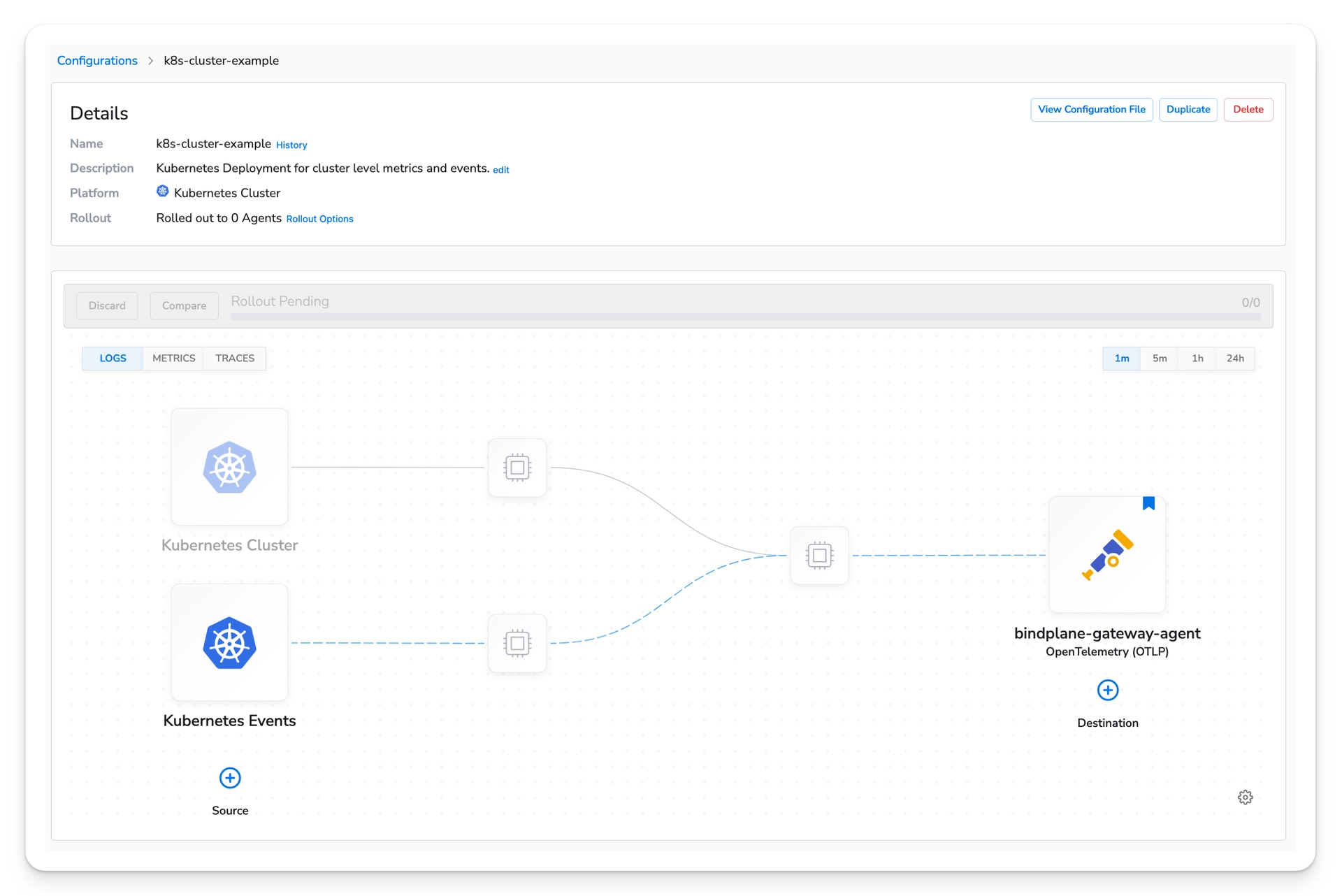
Gateway Configuration
On the Configurations page, choose "Create Configuration". Create a Kubernetes Gateway configuration. The gateway configuration will be deployed as a StatefulSet.
NOTE
Deployment with HPA will be supported in the future, as an alternative to StatefulSet.
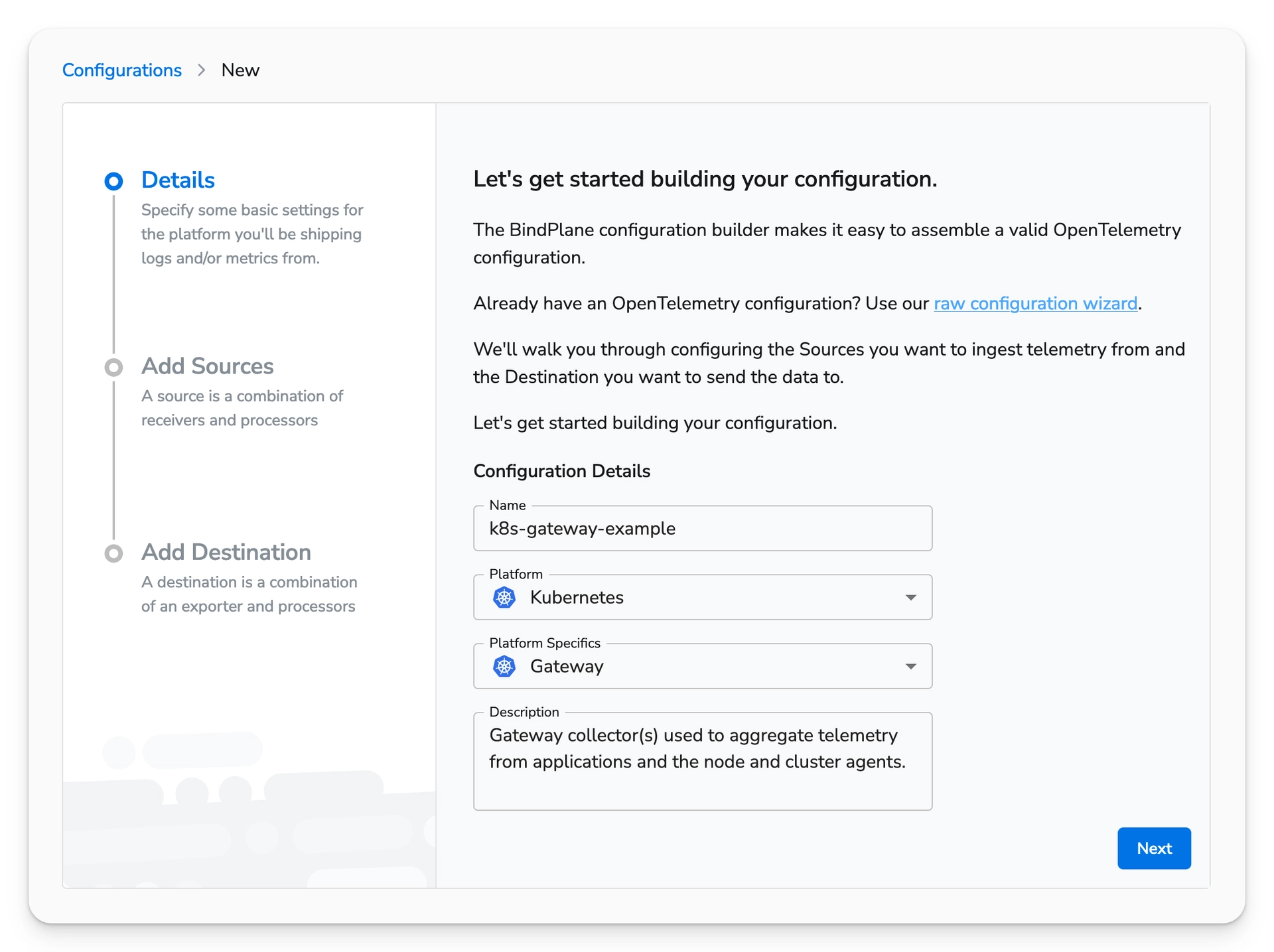
Choose next to view the list of available sources. Select the OpenTelemetry (OTLP) source. The default values will match the values used by the previously created OpenTelemetry destination. This will allow the Gateway Agent to receive telemetry from the other agents.
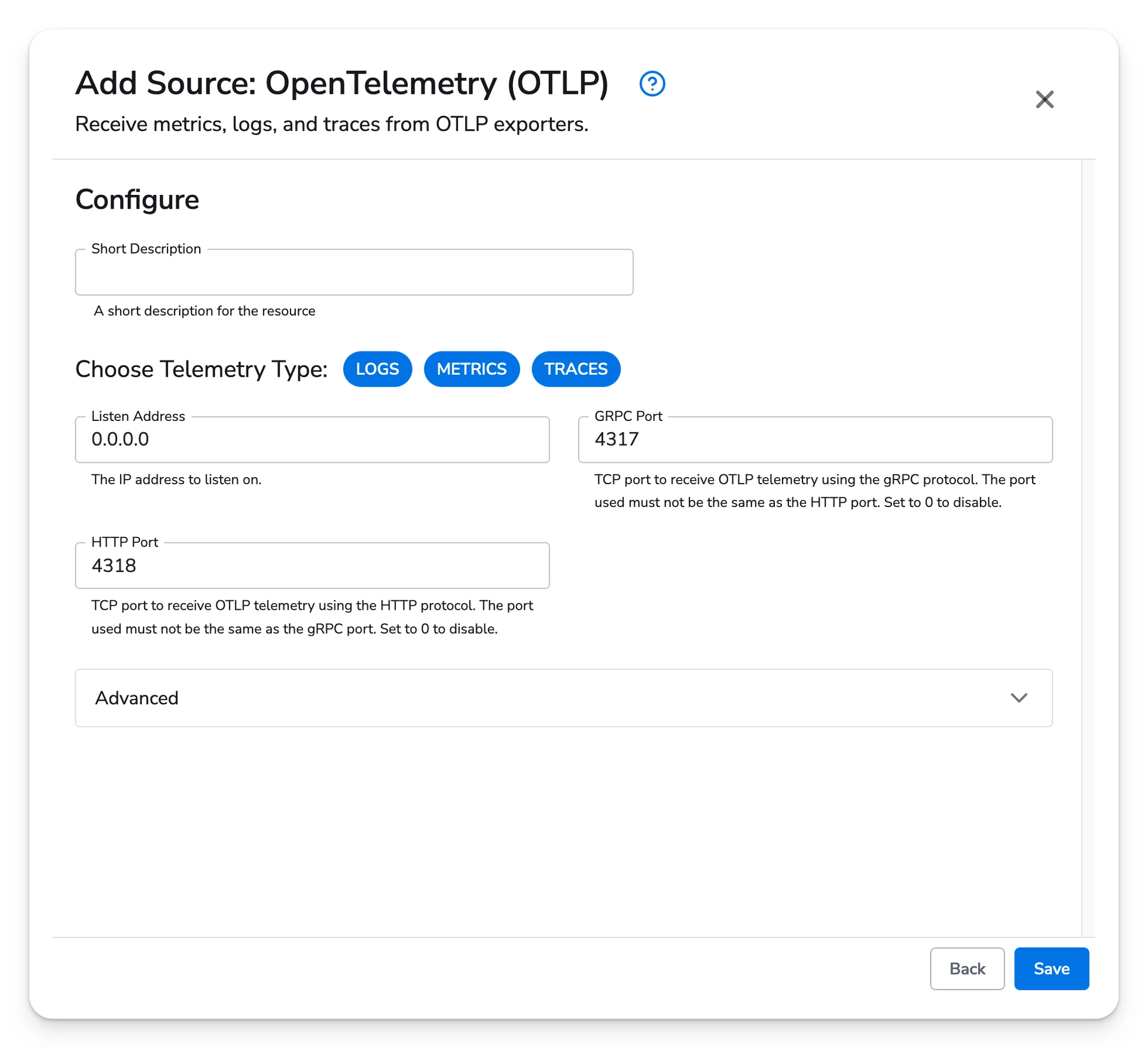
After saving the source, choose next to move to the destination configuration page.
In this example, I am going to use the Google Cloud destination. Feel free to choose the destination
that best fits your environment. If you do not have a destination at this time, you can use the custom
destination and configure the logging exporter. This exporter will act as a "no-op", and allow you
to test the configuration without shipping telemetry to a real destination.
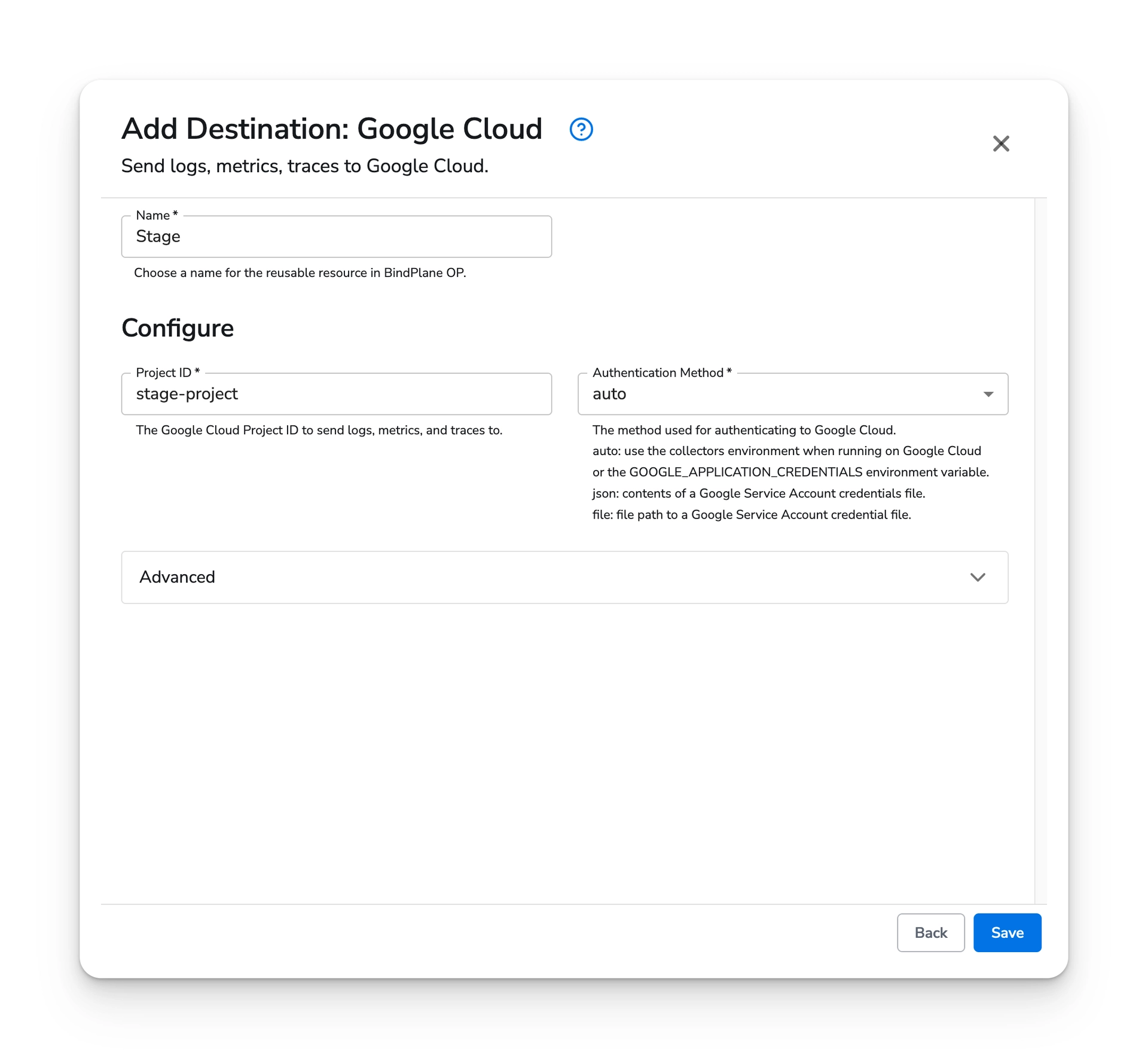
Example Google Cloud destination:
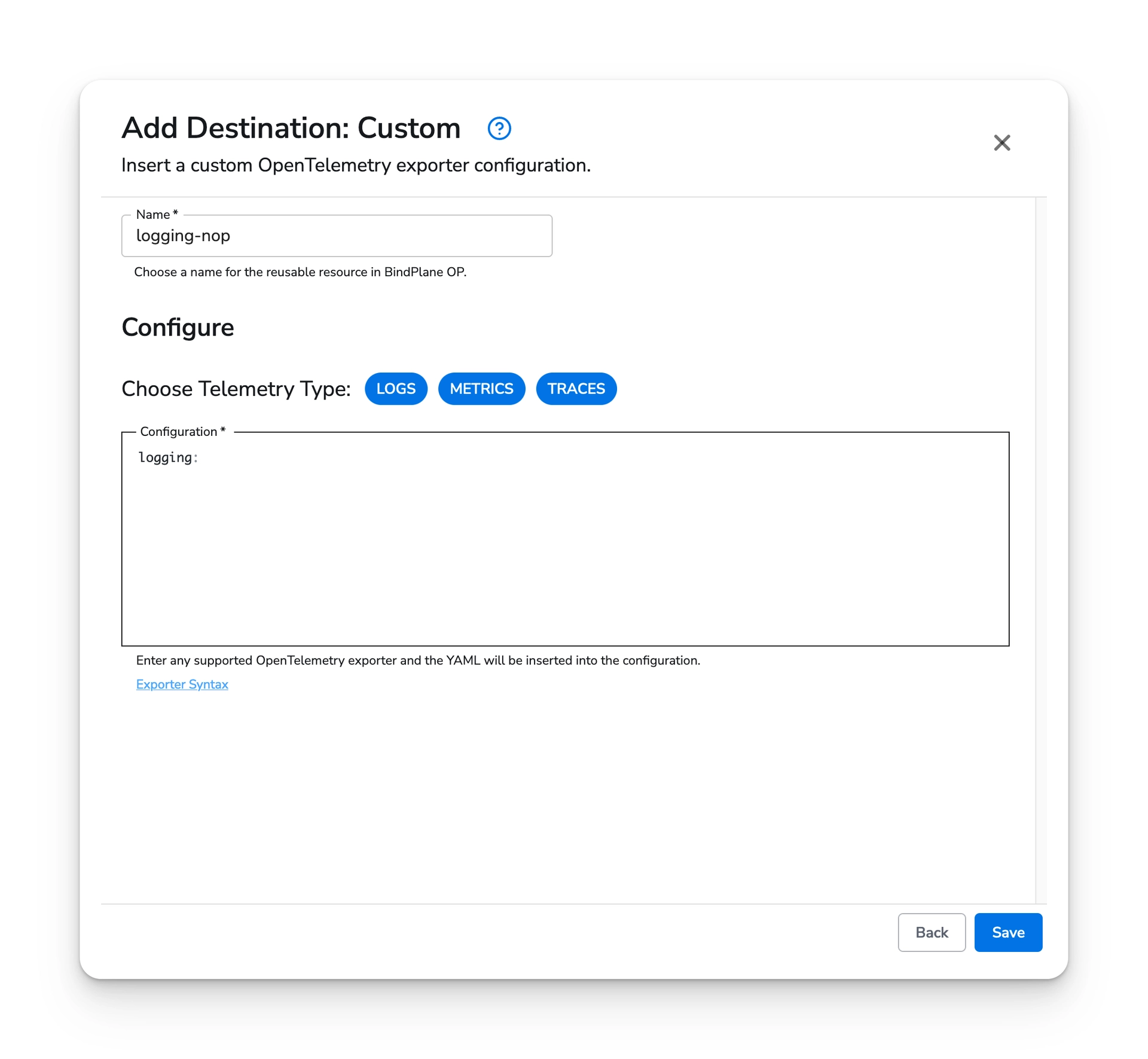
If you would like to use the custom destination, enable all three telemetry options and include the following for the configuration block:
Example Logging destination:
Once you have configured the destination, choose "Save".
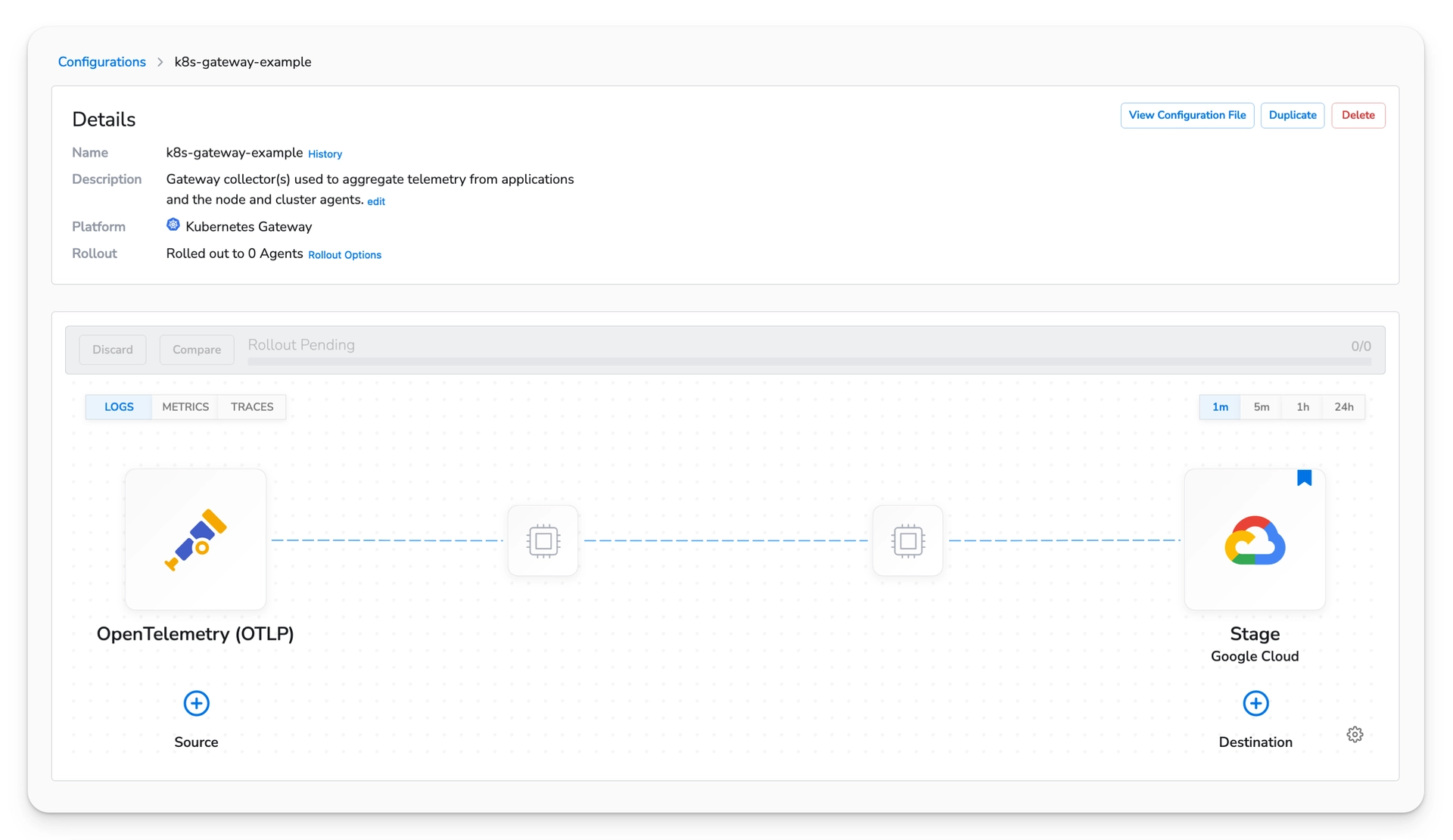
You will be presented with the new pipeline.
If you would like to detect the Kubernetes Cluster name, you can use the resource detection processor.
NOTE
Cluster name detection is available for Google GKE only. Support for Amazon EKS and Azure AKS is coming soon.
Add a processor to the source side of the pipeline by clicking on the processor icon (It can be found between the source icon and the destination icon).
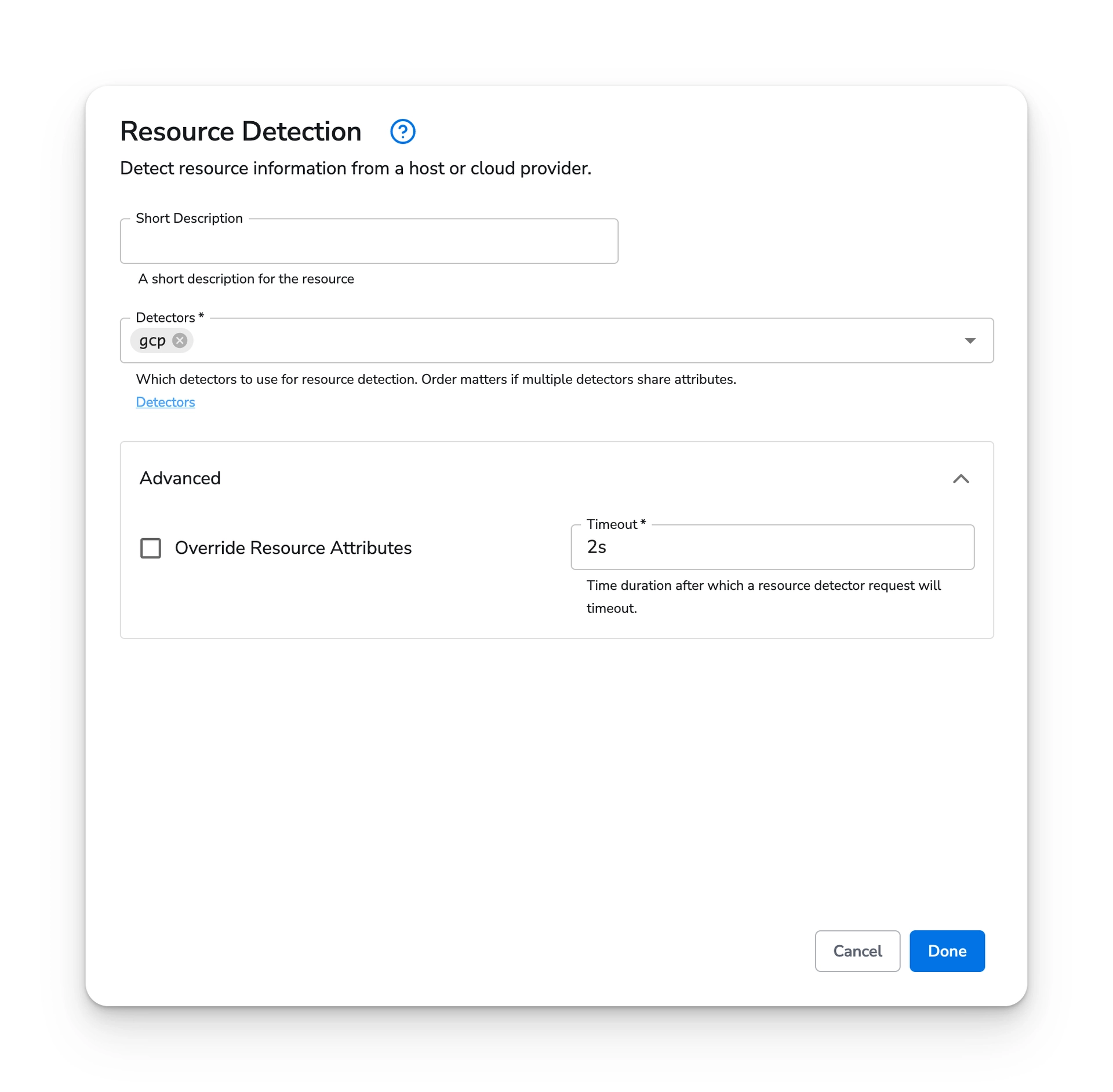
Choose "Add Processor" and search for "Resource Detection".
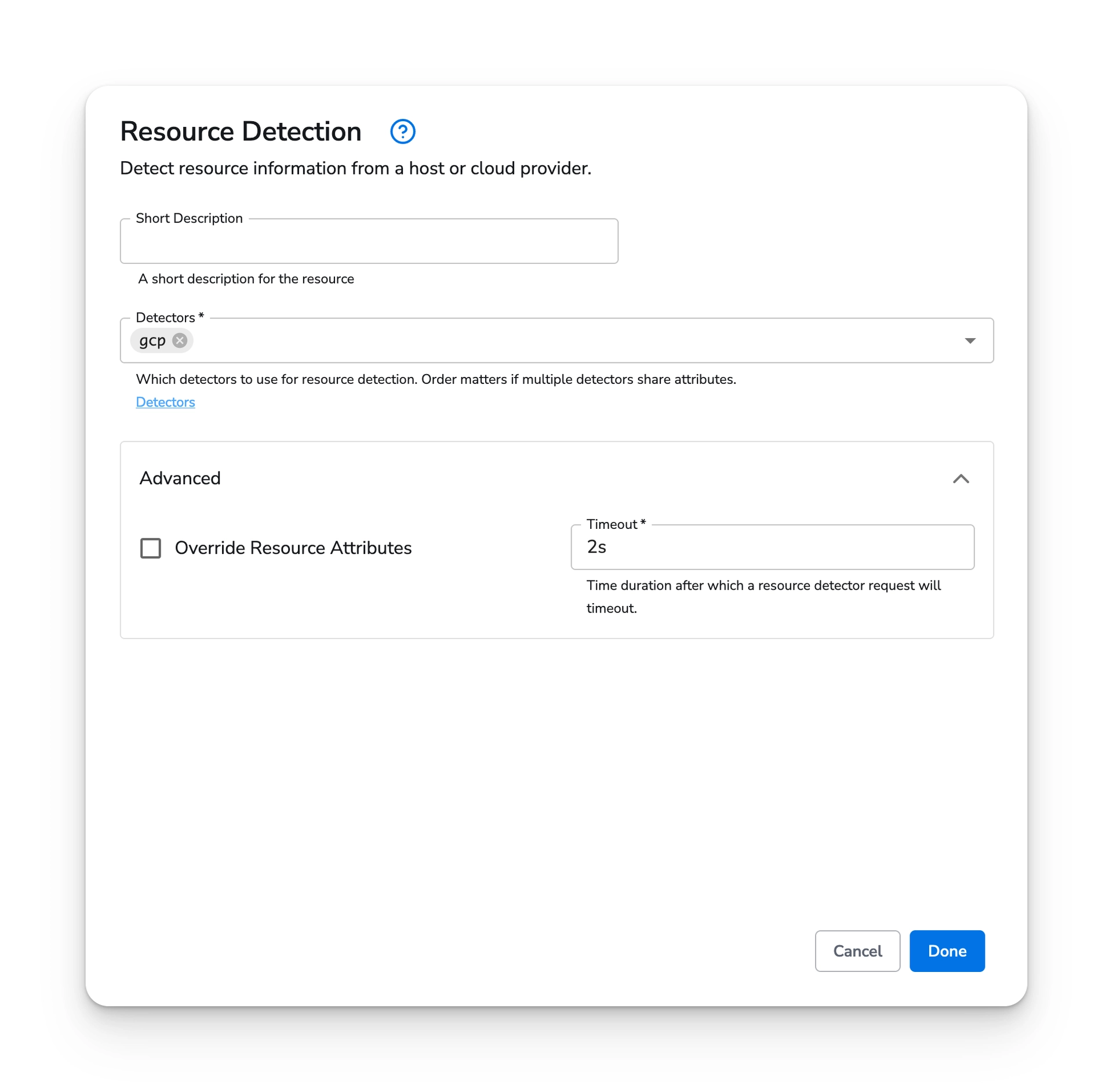
Choose "Done" and then "Save".
Deploy Collectors
Once the configurations are created, you can move on to deploying agents.
Retrieve YAML Manifests
On the Collectors page, select the "Install Collector" button.
Choose the Kubernetes Node platform and the Kubernetes Node configuration you created earlier.
Select "Next" and you will be presented with a yaml text box. Choose "Copy" and save the contents
to a file named bindplane-node-agent.yaml
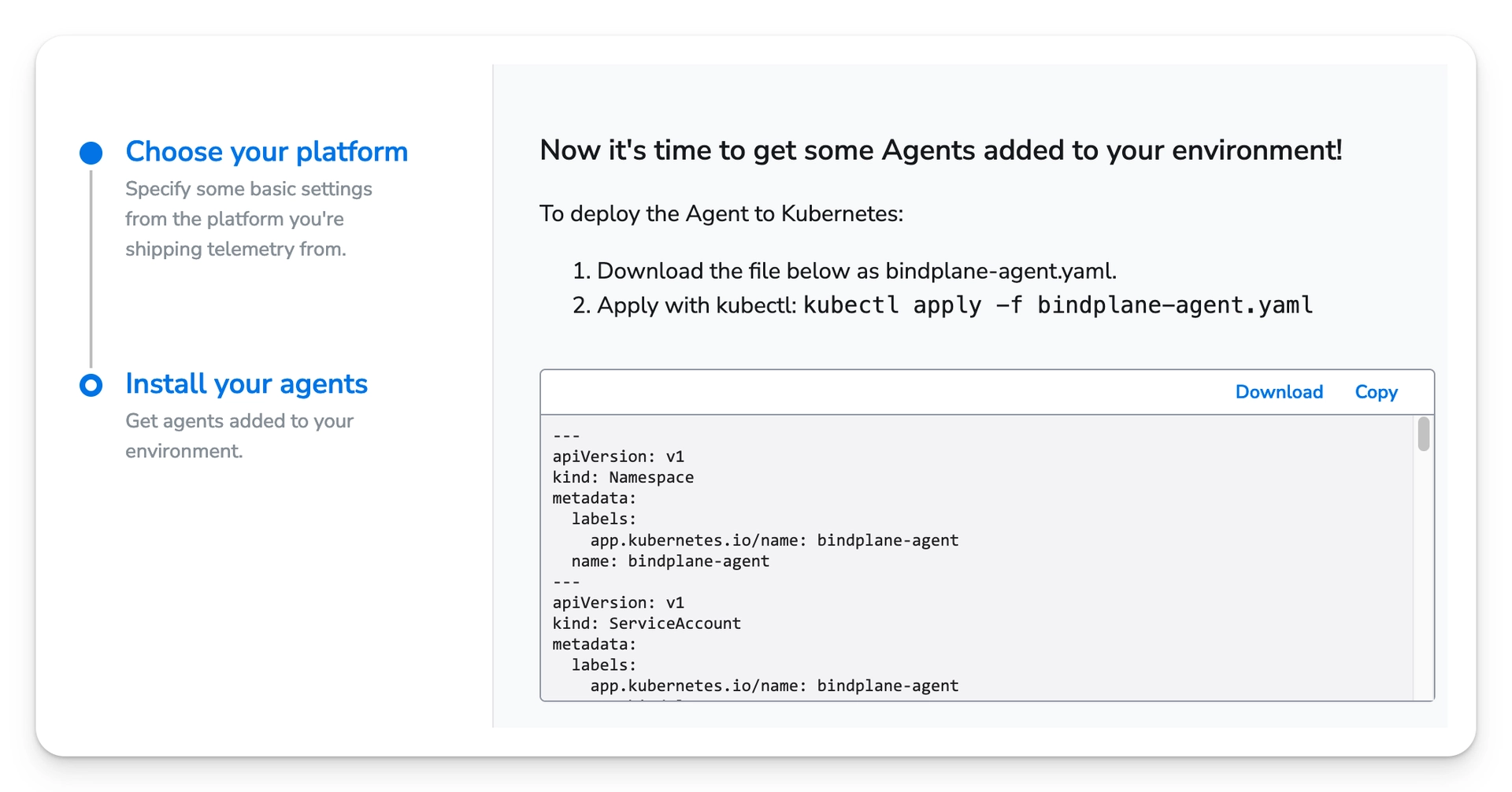
Repeat these steps for the Cluster and Gateway agents. Save their yaml output to files namedbindplane-cluster-agent.yaml and bindplane-gateway-agent.yaml.
Kubectl Apply
With all three manifests saved, you can apply them with a single command:
The output will look like this:
The following resources are created
Namespace:
bindplane-agentRBAC
Service Account:
bindplane-agentCluster Role:
bindplane-agentCluster Role Binding:
bindplane-agent
Node Agent
clusterIP service:
bindplane-node-agentclusterIP service (headless):
bindplane-node-agent-headlessDaemonSet:
bindplane-node-agent
Cluster Agent
Deployment:
bindplane-cluster-agent
Gateway Agent
clusterIP service:
bindplane-gateway-agentclusterIP service (headless):
bindplane-gateway-agent-headlessDaemonSet:
bindplane-gateway-agent
Once the agents are deployed, they will appear on the Agents page. Agents are named with the following convention:
Node agents take the name of the node they are running on
The Cluster agent takes the name of the underlying pod
Gateway agents take the name of the underlying pod
Initial Configuration Rollout
With the collectors connected, you must perform the initial rollout of the configurations.
Navigate to the Configurations page and select your Gateway configuration. Select the "Start Rollout" button. This will push the first version of the configuration to the collectors.
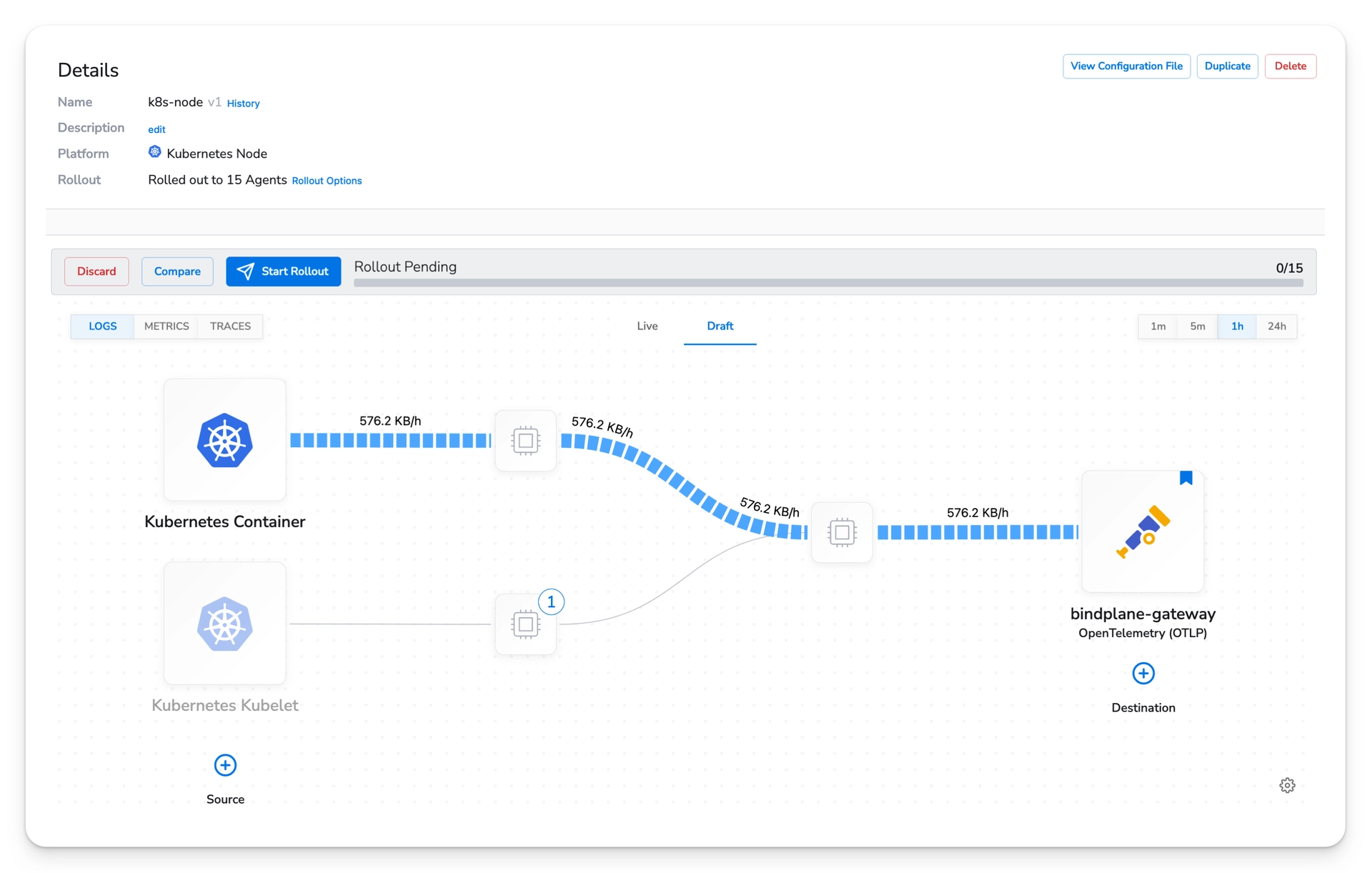
Navigate to the Node and Cluster configurations and trigger their initial rollout.
Once the configurations are rolled out, give them ten minutes to start displaying throughput measurements.
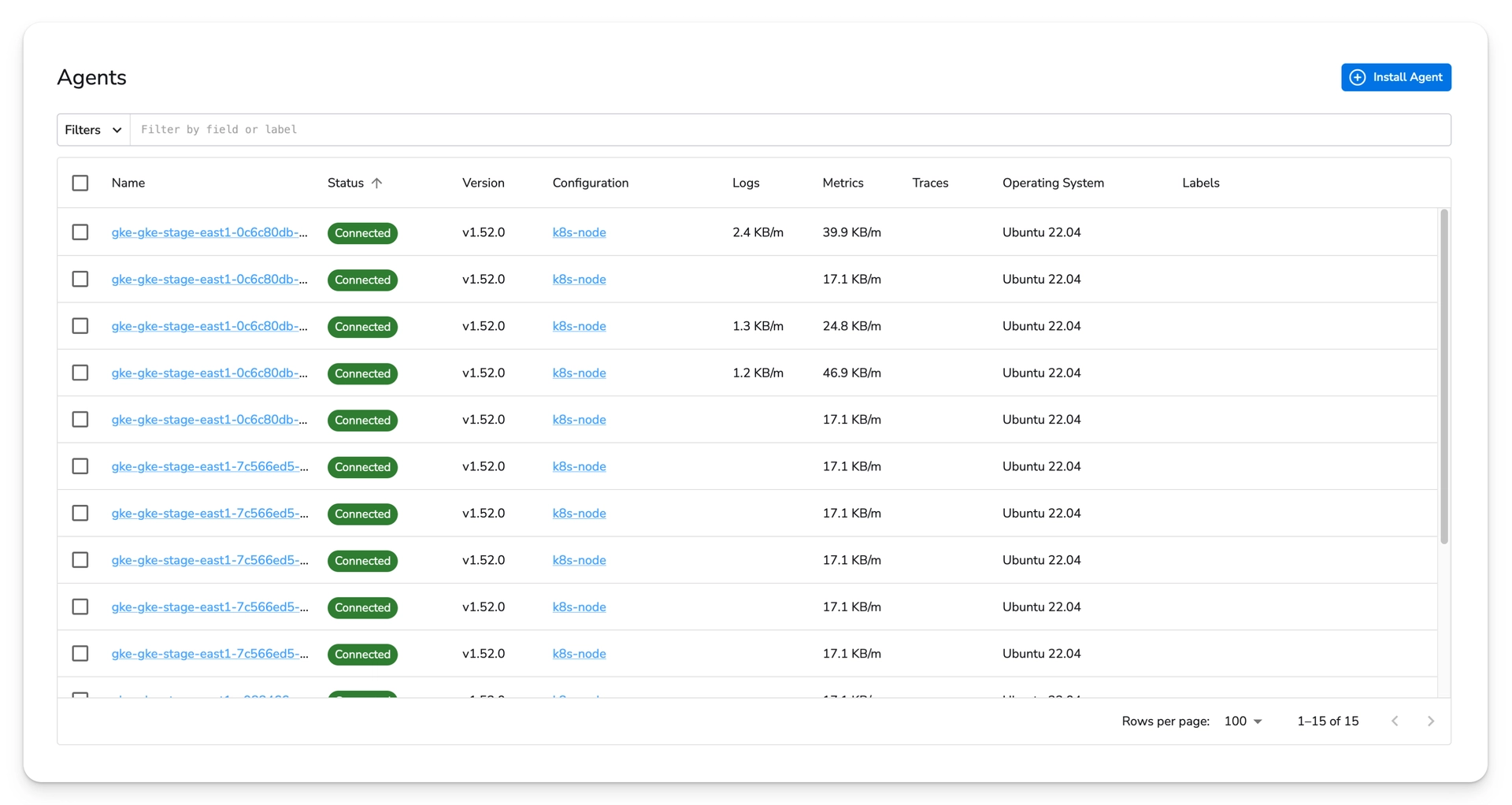
Click on an individual collector and select "Recent Telemetry" to view recent logs and metrics.
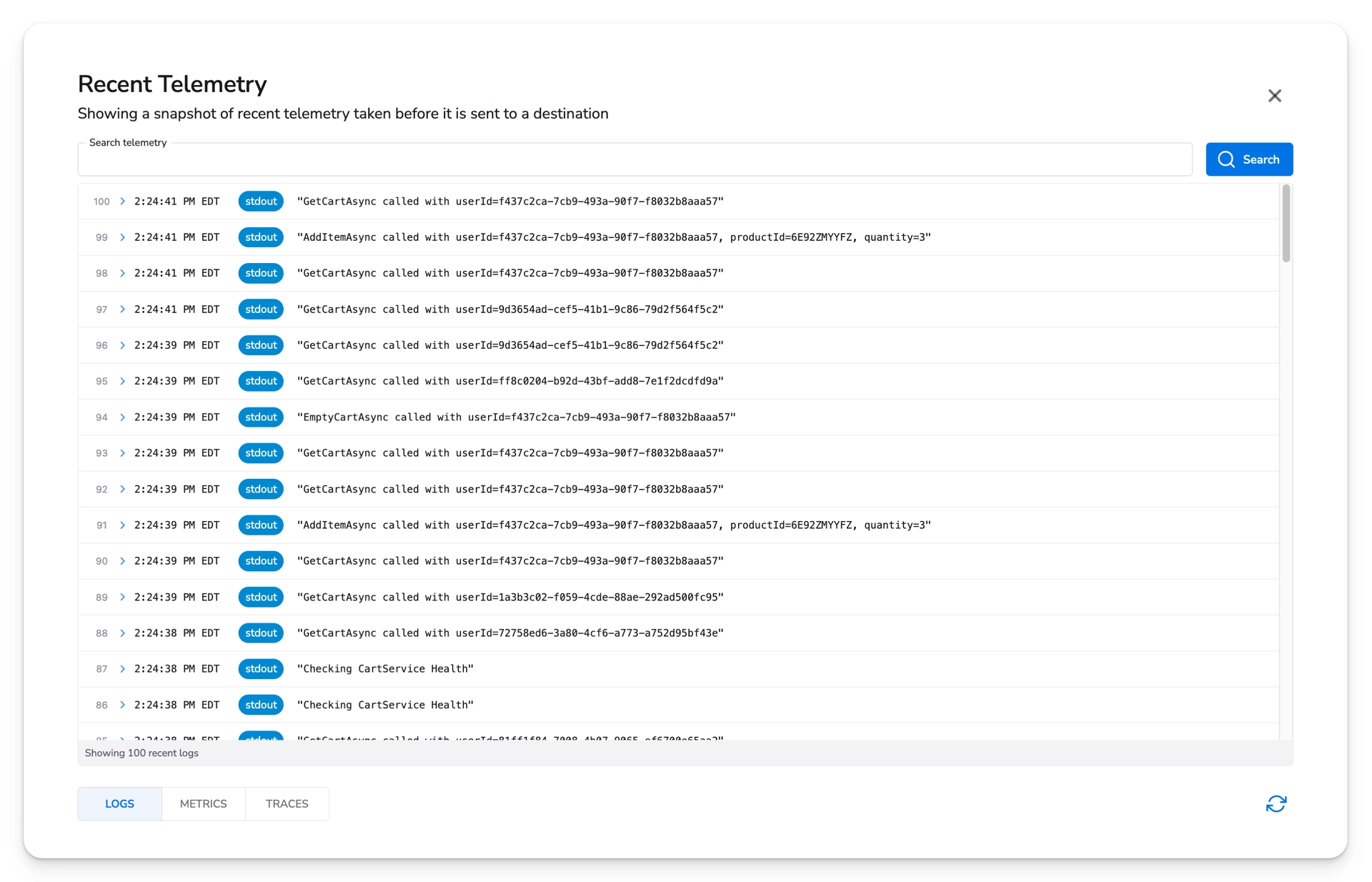
If the collector does not have recent telemetry, try selecting a different one. If activity in the cluster is low, recent telemetry may not be available on every collector right away.
Security
Each agent manifest has a secret key that is used for authentication to Bindplane. If you intend to commit the manifest to git, you should first update the secret key environment variable to use a Kubernetes Secret.
You can create a secret and reference it.
Once the secret value is removed from the manifest, it can be safely committed to git.
Troubleshooting
Collectors do not appear on the Collectors page
If the agent pods are running, but not appearing on the Collectors page, make sure your Bindplane server's remote URL parameter is set correctly.
If operating Bindplane on Linux, check the configuration at /etc/bindplane/config.yaml.
If using Helm to operate Bindplane on Kubernetes, make sure the config.remote_url value is correct.
The Helm chart will set this value to the clusterIP in the Bindplane server's namespace, if it is not set explicitly.
In either case, the remote URL must resolve the Bindplane server and should be reachable by the agents.
If the remote URL appears to be correct, make sure it is correct in the agent manifest.
In this example, the remote URL https://app.bindplane.com:3001 will result in an OpAMP endpoint with value wss://app.bindplane.com:3001/v1/opamp. The OpAMP endpoint is derived from the Bindplane remote URL setting.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I modify the manifests?
A: Yes. You may want to adjust the cpu and memory resource request and limits, as well as affinity rules or pod priority class. You should adjust the manifests to fit your environment.
Q: Can Bindplane Collectors be installed with Helm?
A: Helm is not supported for collector installations. If you are interested in Helm support, please reach out to us through support channels. We would love to have your feedback.
Q: Can Bindplane Collectors be installed with the OpenTelemetry Operator?
A: The OpenTelemetry Operator is not supported for agent installation. The operator only recently added support for OpAMP. We are following the development closely and look forward to supporting the operator in the future.
Q: Is it safe to commit the agent manifests to git?
A: Follow the security section before committing the manifests to git.
Q: Can I use ArgoCD or Flux to manage the agent deployments?
A: Yes. If you have existing tooling in place for managing resources within your cluster, we encourage that you have them handle the agent installation.
Was this helpful?